jupyterhub-pyspark-hdfs-anomaly-detection-taxi-data
This demo showcases the integration between Jupyter and Apache Hadoop deployed on the Stackable Data Platform (SDP) Kubernetes cluster. JupyterLab is deployed using the pyspark-notebook stack provided by the Jupyter community. The SDP makes this integration easy by publishing a discovery ConfigMap for the HDFS cluster. This ConfigMap is then mounted in all Pods` running PySpark notebooks so that these have access to HDFS data. For this demo, the HDFS cluster is provisioned with a small sample of the NYC taxi trip dataset which is analyzed with a notebook that is provisioned automatically in the JupyterLab interface .
This demo can be installed on most cloud managed Kubernetes clusters as well as on premise or on a reasonably provisioned laptop. Install this demo on an existing Kubernetes cluster:
stackablectl demo install jupyterhub-pyspark-hdfs-anomaly-detection-taxi-data|
Some container images used by this demo are quite large and some steps may take several minutes to complete. If you install this demo locally, on a developer laptop for example, this can lead to timeouts during the installation. If this happens, it’s safe to rerun the For more details on how to install Stackable demos see the documentation. |
Aim / Context
This demo does not use the Stackable spark-k8s-operator but rather delegates the creation of executor pods to JupyterHub. The intention is to demonstrate how to interact with SDP components when designing and testing Spark jobs: the resulting script and Spark job definition can then be transferred for use with a Stackable SparkApplication resource. When logging in to JupyterHub (described below), a pod will be created with the username as a suffix e.g. jupyter-admin. This runs a container that hosts a Jupyter notebook with Spark, Java and Python pre-installed. When the user creates a SparkSession, temporary spark executors are created that are persisted until the notebook kernel is shut down or re-started. The notebook can thus be used as a sandbox for writing, testing and benchmarking Spark jobs before they are moved into production.
Overview
This demo will:
-
Install the required Stackable Data Platform operators
-
Spin up the following data products
-
JupyterHub: A multi-user server for Jupyter notebooks
-
Apache HDFS: A distributed file system used to store the taxi dataset
-
-
Download a sample of the NY taxi dataset into HDFS
-
Install Jupyter notebook
-
Train an anomaly detection model using PySpark on the data available in HDFS
-
Perform some predictions and visualize anomalies
HDFS
The Stackable Operator for Apache HDFS will spin up a HDFS cluster in order to store the taxi dataset in Apache Parquet format. This dataset will be read and processed via PySpark.
Before trying out the notebook example in Jupyter, check if the taxi data was loaded to HDFS successfully:
$ kubectl exec -c namenode -it hdfs-namenode-default-0 -- /bin/bash -c "./bin/hdfs dfs -ls /ny-taxi-data/raw"
Found 1 items
-rw-r--r-- 3 stackable supergroup 314689382 2022-11-23 15:01 /ny-taxi-data/raw/fhvhv_tripdata_2020-09.parquetThere should be one parquet file containing taxi trip data from September 2020.
JupyterHub
Have a look at the available Pods before logging in (operator pods are left out for clarity, you will see more Pods):
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
continuous-image-puller-87dzk 1/1 Running 0 29m
continuous-image-puller-8qq7m 1/1 Running 0 29m
continuous-image-puller-9xbss 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-datanode-default-0 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-journalnode-default-0 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-namenode-default-0 2/2 Running 0 29m
hdfs-namenode-default-1 2/2 Running 0 28m
hub-66c6798b9c-q877t 1/1 Running 0 29m
load-test-data-wsqpk 0/1 Completed 0 25m
proxy-65955f56cf-tf4ns 1/1 Running 0 29m
user-scheduler-8d888c6d4-jb4mm 1/1 Running 0 29m
user-scheduler-8d888c6d4-qbqkq 1/1 Running 0 29mJupyterHub will create a Pod for each active user. In order to reach the JupyterHub web interface, create a port-forward:
$ kubectl port-forward service/proxy-public 8080:httpNow access the JupyterHub web interface via:
http://localhost:8080
You should see the JupyterHub login page.
Log in with username admin and password adminadmin.
There should appear a new pod called jupyter-admin (operator pods are left out for clarity, you will see more Pods):
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
continuous-image-puller-87dzk 1/1 Running 0 29m
continuous-image-puller-8qq7m 1/1 Running 0 29m
continuous-image-puller-9xbss 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-datanode-default-0 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-journalnode-default-0 1/1 Running 0 29m
hdfs-namenode-default-0 2/2 Running 0 29m
hdfs-namenode-default-1 2/2 Running 0 28m
hub-66c6798b9c-q877t 1/1 Running 0 29m
jupyter-admin 1/1 Running 0 20m
load-test-data-wsqpk 0/1 Completed 0 25m
proxy-65955f56cf-tf4ns 1/1 Running 0 29m
user-scheduler-8d888c6d4-jb4mm 1/1 Running 0 29m
user-scheduler-8d888c6d4-qbqkq 1/1 Running 0 29mYou should arrive at your workspace:
Now you can click on the notebooks folder on the left and open the contained file and run it. Click on the double arrow to execute the Python scripts. You can inspect the hdfs folder as well where the core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml from the discovery ConfigMap of the HDFS cluster are located.
|
The image defined for the spark job must contain all dependencies needed for that job to run. For pyspark jobs, this will mean that python libraries either need to be baked into the image itself (this demo contains a Dockerfile that was used to generate a image containing scikit-learn, pandas and their dependencies), or packaged some other way. |
Model details
The job uses an implementation of the Isolation Forest algorithm provided by the scikit-learn library: the model is trained and then invoked by a user-defined function (see this article for how to call the sklearn library with a pyspark UDF), all of which is run using the Spark executors spun up in the current SparkSession. This type of model attempts to isolate each data point by continually partitioning the data. Data closely packed together will require more partitions to separate data points, whereas any outliers will require less: the number of required partitions for a particular data point is thus inversely proportional to the anomaly "score".
Visualization
The notebook shows how to plot the outliers against a particular metric (e.g. "number of rides"):
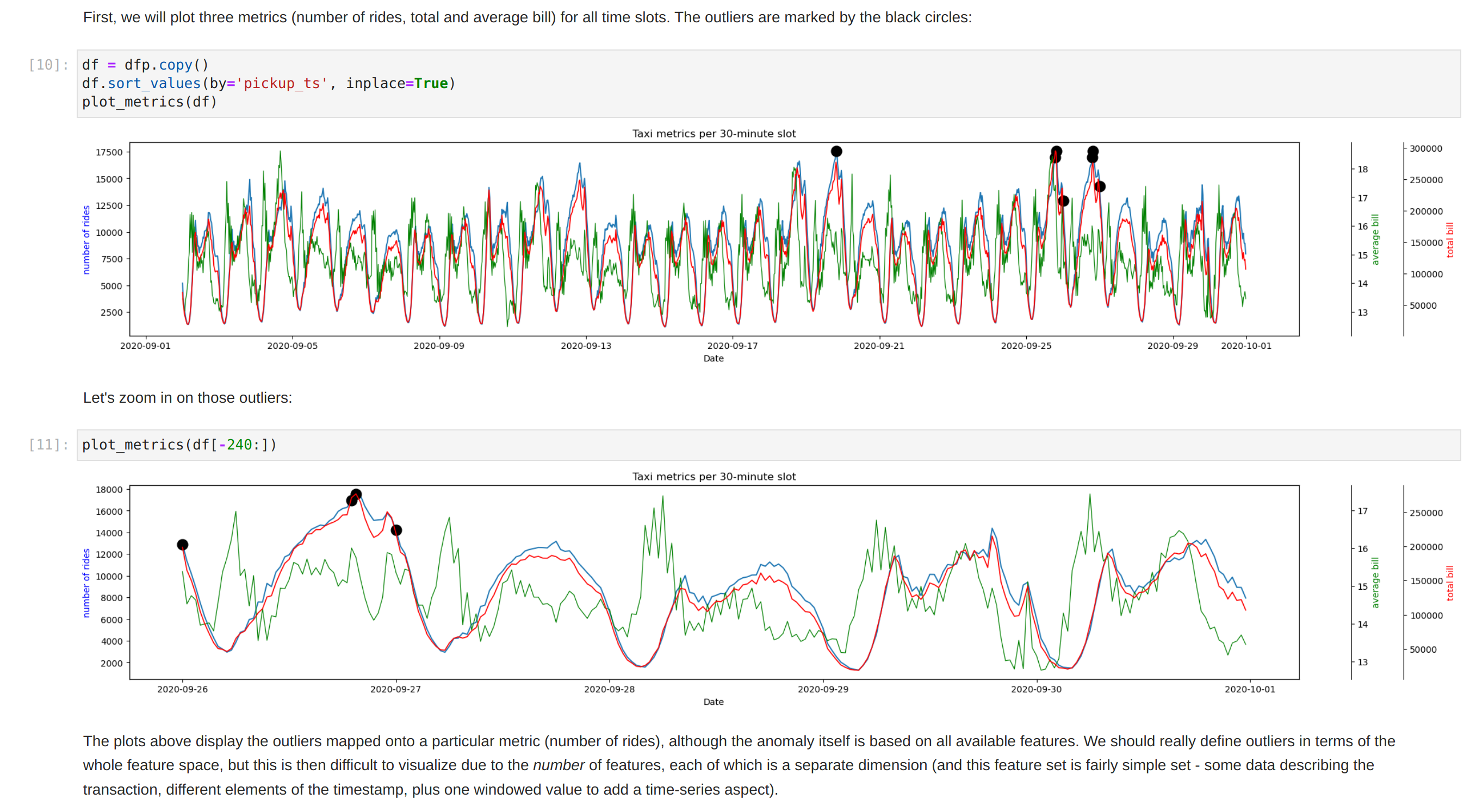
However, this is mainly for convenience - the anomaly score is derived from the entire feature space i.e. it takes all dimensions (or features/columns) into account when scoring data. This means that not only are the results difficult to visualize (how can multidimensional data be represented in only 3-D dimensional space?), but that a root cause analysis has to be a separate process. It would be tempting to look at just one metric and assume causal affects, but the model "sees" all features as a set of numerical values and derives patterns accordingly.
We can tackle the first of these issues by collapsing - or projecting - our data down into a manageable number of dimensions that can be plotted: once the script has finished successfully, plots should be displayed on the bottom that show the same data in 2D and 3D representation. The 3D plot should look like this:
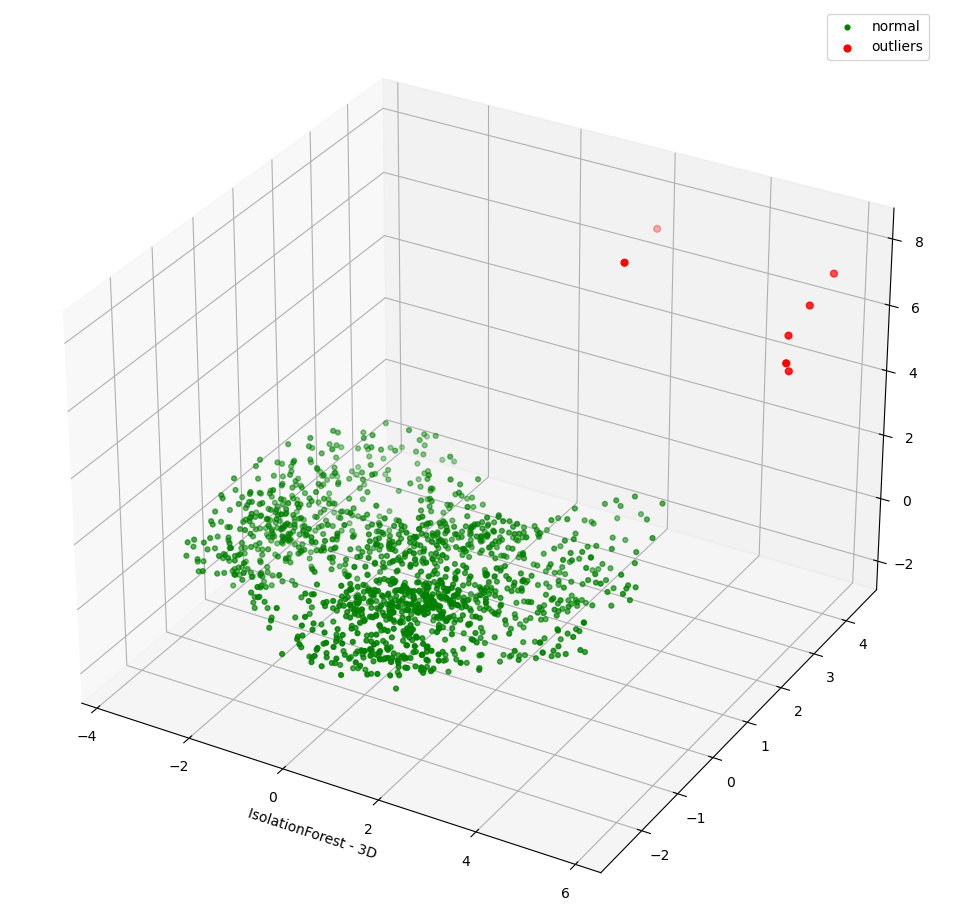
It is clear that the model has detected outliers even though that would not have been immediately apparent from the time-series representation alone.